Thursday 29th January
Grammar
Thursday 29th January 2026
LC: To use the conjunction 'if' within a complex sentence.
What conjunction have we been using in our complex sentences?
On your whiteboards:
Choose a word below, think of and write a complex sentence. Your complex sentences must include the subordinating conjunction 'if'.
- measure
- treasure
- creature
Main
LC: To recognise some additional forms of poetry.
There are many different forms of poetry. We are going to look at three different types of poems today.
Acrostic Poems
- Definition: The first letter of each line spells out a word or message, often the topic of the poem.
- Example:
- Cats love to nap in the sun.
Always curious, they explore.
Tail flicks when they're playful.
Soft purrs make us smile.
Haiku (Japanese Poetry)
- Definition: A three-line poem with a syllable structure of 5-7-5. Often about nature.
- Example: The bright sun rises (5 syllables)
A flower blooms in silence (7 syllables)
Spring is here today. (5 syllables)
Narrative Poems
- Definition: It tells a story, often with rhyme and rhythm.
- Example:
One bright and sunny afternoon,
I held a big red balloon.
It tugged and pulled, high in the air,
And then slipped loose—I stood and stared.
The wind it caught my precious prize,
It floated up into the skies.
"Come back!" I cried, but it was gone,
It flew and flew till nearly dawn.
I saw it drift past hills and trees,
It danced above the deep blue seas.
A bird flew by and gave a squawk,
Then perched upon a floating rock.
By morning, it began to fall,
A tiny speck, so round and small.
And as I watched, what did I see?
It landed gently back near me!
Talk Partners
Discuss which poem you like the most.
Why do you like it? Does it have rhyming words? What about the rhythm?
Whole Class
We are going to focus on narrative poetry today! When we read a poem what do we need to be aware of? What tells us when to stop or take a breath?
As a class we are going to read the below narrative poem, highlight the words that rhyme and the punctuation.
The Lost Balloon
Milly was playing one warm summer’s day,
When her red balloon floated away.
Up it went, into the sky,
“Come back!” she called. “You can’t say goodbye!”
The balloon drifted higher, caught in the breeze,
Sailing past birds and over tall trees.
Milly ran fast, her feet in a dash,
But the balloon flew far in a hurried flash.
“Oh no,” Milly sighed, her face full of gloom,
“I guess my red balloon is lost to the moon.”
Just then, a boy on a bike came by,
With the red balloon, caught on a tie!
“Is this yours?” he asked with a grin.
Milly laughed and twirled, her joy from within.
“Thank you!” she cheered, hugging it tight.
Her balloon was back, and all felt right.
So Milly learned on that sunny afternoon,
Sometimes lost things can come back soon.
Activity
First, you will read the below poem.
Next, you will highlight words that rhyme in one colour.
Then, you will highlight the punctuation in another colour.
The Brave Little Mouse
In a tiny hole beneath the floor,
Lived a mouse who wanted to explore.
"I’ll see the world and cross the stream,
And find the land of cheese and cream!"
He packed a crumb of bread and cheese,
And scampered off beneath the trees.
A cat appeared! The mouse turned pale,
He raced away, across the trail.
Through fields and hills, the mouse did roam,
Until he missed his cozy home.
“I’ll see the world another day,
But now it’s time to find my way.”
Read the poem aloud taking note of the punctuation.
Remember tone, intonation and volume!
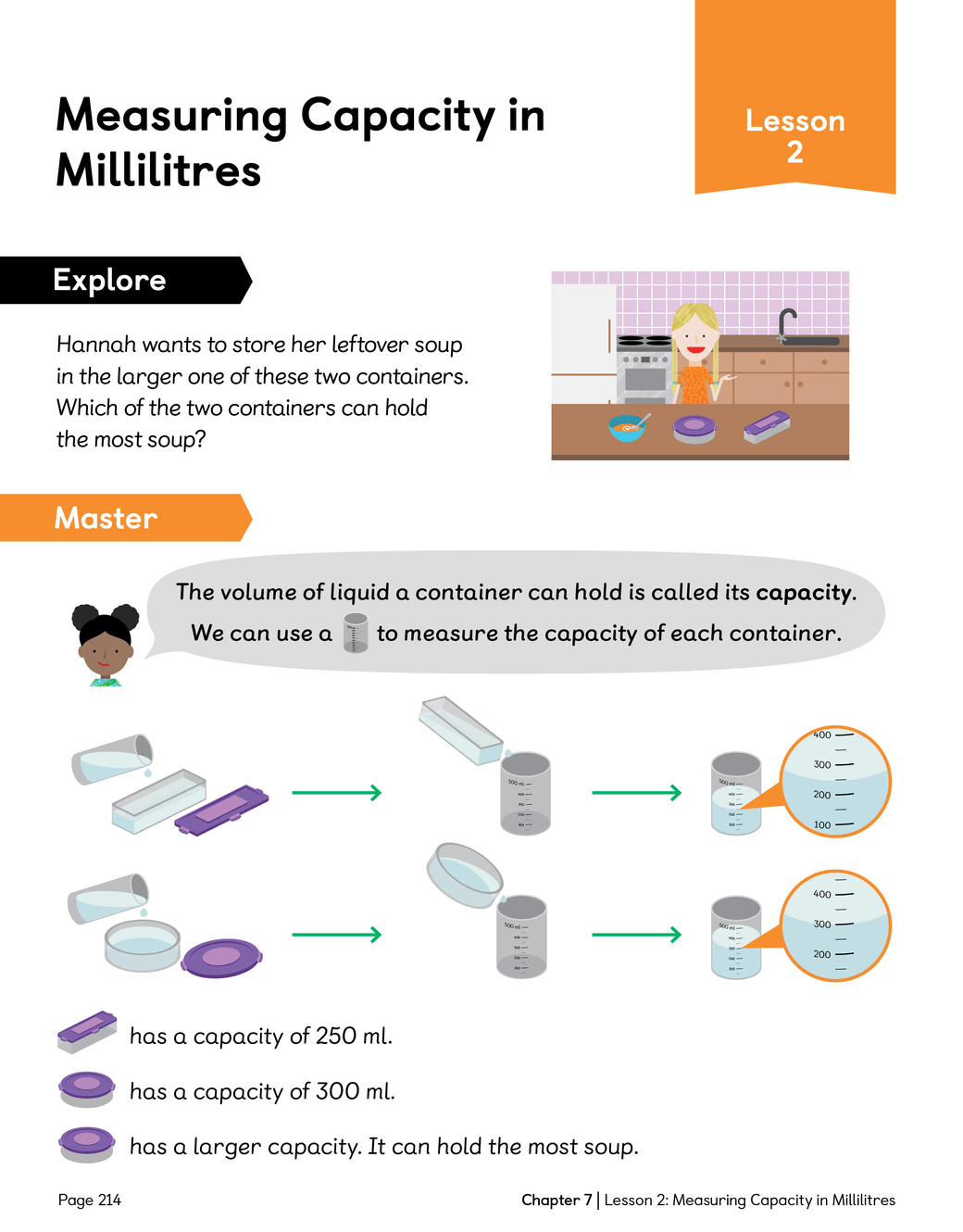
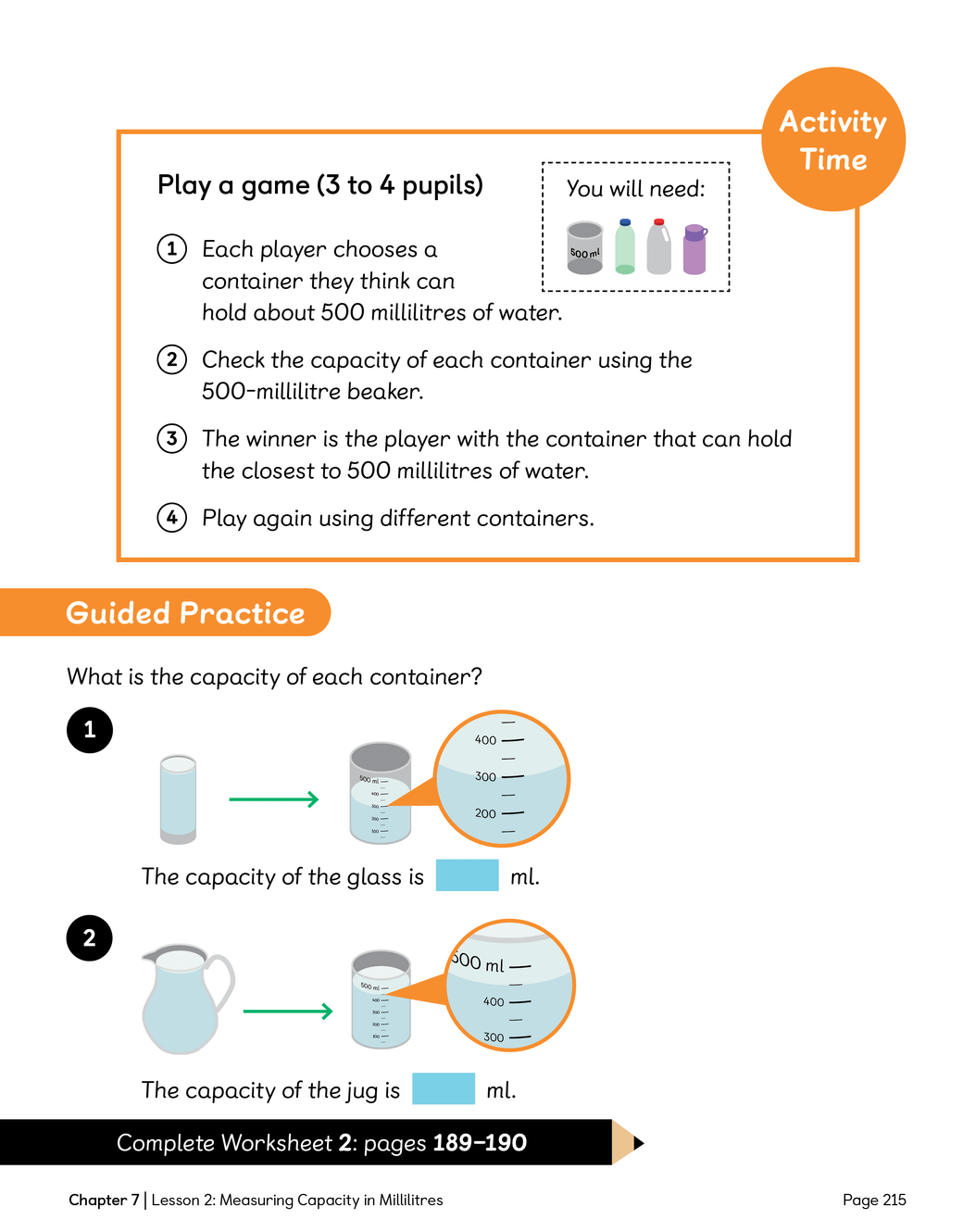
LC: To be able to measure capacity in millilitres.
RIC

R - What did one of the otters slap?
I - What do you predict will happen next?
C - Why do you think the author has chosen to write short sentences in the last paragraph?
Thursday 29th January 2026
LC: To identify the main ideas drawn from more than one paragraph.
The main idea is the most important idea in a paragraph. Ask yourself, what is the paragraph telling me?
Talk Partners
What could help you identify the main idea? Think about your learning from the past two reading lessons this week.
Whole Class
What does summarise mean?
We are going to read the paragraphs below and combine the main ideas from each paragraph to form a summary.
Paragraph 1:
Dogs are friendly animals. They love to play with their owners and are often called "man's best friend." Many people keep dogs as pets because they are loyal and good companions.
Paragraph 2:
Dogs come in many different sizes and colours. Some are small, like Chihuahuas, while others are big, like Great Danes. Each breed has its own special characteristics.
What is the main idea?
Paragraph 1:
Plants need water, sunlight, and soil to grow. These things help the plant stay healthy. Without water, a plant will wilt and die.
Paragraph 2:
It is important to water plants regularly. If you water them too much, though, the plant may get sick. Finding the right balance is key to keeping the plant strong and healthy.
What is the main idea?
Activity
Paragraph 1:
In the winter, the weather can be very cold. Many animals grow thick fur to keep warm. Some animals, like bears, sleep through the cold months in a process called hibernation.
Paragraph 2:
People also wear warm clothes in winter to stay cozy. Jackets, hats, and gloves are important to protect us from the cold. In snowy places, people often use scarves and boots.
What is the main idea?
LC: To identify the main achievements during the Stone Age.



Let's have a quick re-cap.
It's easier to think of the Stone Age to be like a sandwich, because it can be separated in to 3 stages:

What can you remember from the Paleolithic Era and the Mesolithic Era. Circle the correct answers on your worksheet.

This week we are learning about the Neolithic Era which began approximately 6000 years ago! Here are some keywords for us to think about:

Now that early humans had fire and tools to hunt animals, they began farming...
They also began to grow crops such as wheat and barley.

Their houses became more advanced...


Now that we know that the early humans had flint to make a fire, clay to make pots, tools to catch animals and plant seeds.
Can you compare life from the Neolithic Era to the Mesolithic and Paleolithic Era?
Compared to the Paleolithic Era and the Mesolithic Era, humans became more advanced and could make...